These are functions run in the context of their own FreeRTOS threads. More...

|
Modules | |
| Helpers | |
| Helper functions to help the read-ability of freertos.cpp. | |
Functions | |
| void | StartCommandTask (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the commandTask thread. It initializes all data structures and peripheral devices associated with the application, and then assumes responsibility for distributing commands to the actuators. More... | |
| void | StartUART1Task (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the UART1_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART1, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task. More... | |
| void | StartUART2Task (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the UART2_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART2, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task. More... | |
| void | StartUART3Task (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the UART3_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART3, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task. More... | |
| void | StartUART4Task (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the UART4_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART4, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task. More... | |
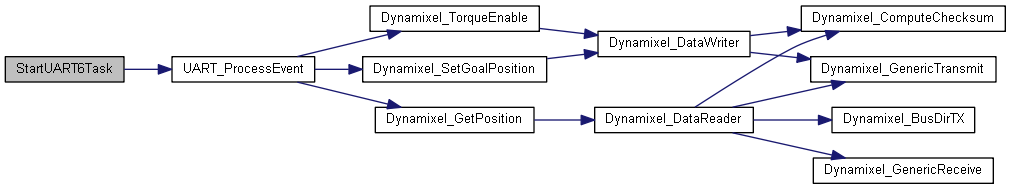
| void | StartUART6Task (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the UART6_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART6, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task. More... | |
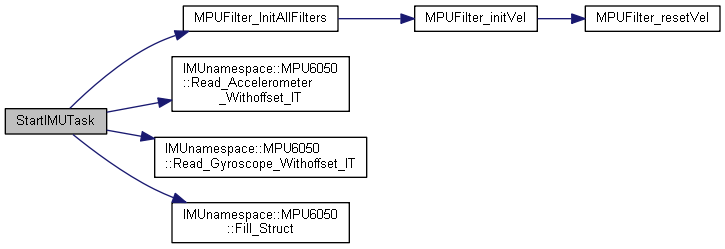
| void | StartIMUTask (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the IMUTask thread. During each control cycle, this thread fetches accelerometer and gyroscope data, then sends this data to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task. More... | |
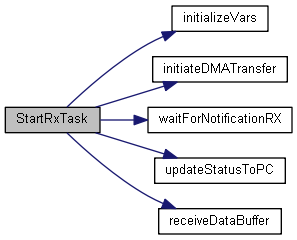
| void | StartRxTask (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the RxTask thread. It initiates DMA-based receptions of RobotGoals from the PC via UART5. Upon successful reception of a RobotGoal, the UARTx_ and IMUTask threads are unblocked. More... | |
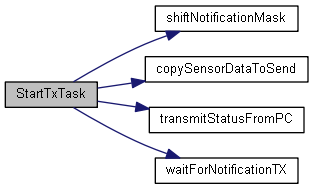
| void | StartTxTask (void const *argument) |
| This function is executed in the context of the TxTask thread. This thread is blocked until all sensor data has been received through the sensor queue. After this time, the UARTx_ and IMUTask will be blocked. Then, a DMA-based transmission of a RobotState is sent to the PC via UART5. More... | |
Detailed Description
These are functions run in the context of their own FreeRTOS threads.
Function Documentation
◆ StartCommandTask()
| void StartCommandTask | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the commandTask thread. It initializes all data structures and peripheral devices associated with the application, and then assumes responsibility for distributing commands to the actuators.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 328 of file freertos.cpp.

◆ StartIMUTask()
| void StartIMUTask | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the IMUTask thread. During each control cycle, this thread fetches accelerometer and gyroscope data, then sends this data to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 655 of file freertos.cpp.
◆ StartRxTask()
| void StartRxTask | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the RxTask thread. It initiates DMA-based receptions of RobotGoals from the PC via UART5. Upon successful reception of a RobotGoal, the UARTx_ and IMUTask threads are unblocked.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 713 of file freertos.cpp.
◆ StartTxTask()
| void StartTxTask | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the TxTask thread. This thread is blocked until all sensor data has been received through the sensor queue. After this time, the UARTx_ and IMUTask will be blocked. Then, a DMA-based transmission of a RobotState is sent to the PC via UART5.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 738 of file freertos.cpp.
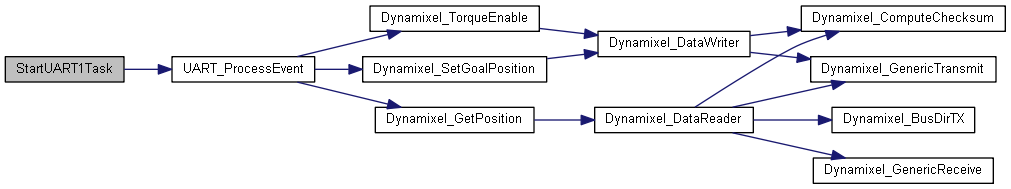
◆ StartUART1Task()
| void StartUART1Task | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the UART1_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART1, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 506 of file freertos.cpp.
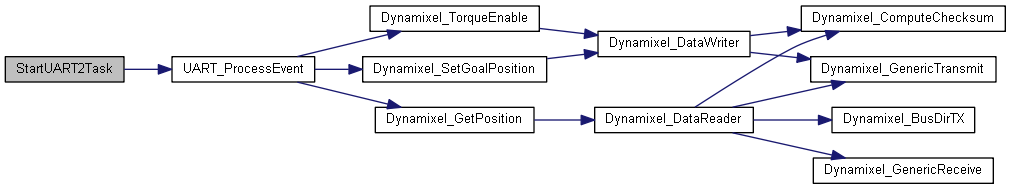
◆ StartUART2Task()
| void StartUART2Task | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the UART2_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART2, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 536 of file freertos.cpp.
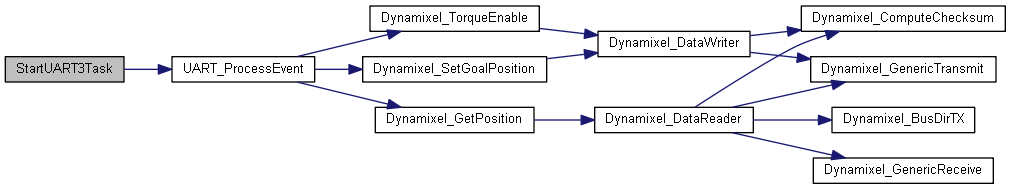
◆ StartUART3Task()
| void StartUART3Task | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the UART3_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART3, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 566 of file freertos.cpp.
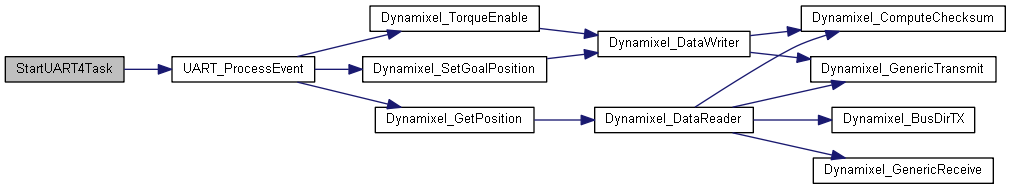
◆ StartUART4Task()
| void StartUART4Task | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the UART4_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART4, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 596 of file freertos.cpp.
◆ StartUART6Task()
| void StartUART6Task | ( | void const * | argument | ) |
This function is executed in the context of the UART6_ thread. It processes all commands for the motors physically connected to UART6, and initiates the I/O calls to them. Whenever it processes read commands for a motor, it sends the data received to the multi-writer sensor queue, which is read only by the TX task.
This function never returns.
Definition at line 626 of file freertos.cpp.