Interfaces for previously-defined functions. More...
|
Functions | |
| void | Dynamixel_EnterWheelMode (Dynamixel_HandleTypeDef *hdynamixel, float goalVelocity) |
| Sets the control registers such that the rotational angle of the motor is not bounded. More... | |
| void | Dynamixel_EnterJointMode (Dynamixel_HandleTypeDef *hdynamixel) |
| Sets the control registers such that the rotational angle of the motor is constrained between the default values. More... | |
Detailed Description
Interfaces for previously-defined functions.
Interfaces for previously-defined functions
This subsection provides a set of functions which implement functions which call previously-defined functions in order to accomplish specific tasks.
Function Documentation
◆ Dynamixel_EnterJointMode()
| void Dynamixel_EnterJointMode | ( | Dynamixel_HandleTypeDef * | hdynamixel | ) |
Sets the control registers such that the rotational angle of the motor is constrained between the default values.
- Parameters
-
hdynamixel pointer to a Dynamixel_HandleTypeDef structure that contains the configuration information for the motor
- Returns
- None
Definition at line 1037 of file DynamixelProtocolV1.c.

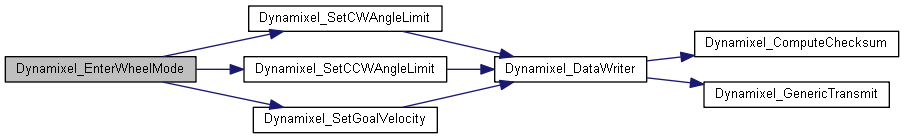
◆ Dynamixel_EnterWheelMode()
| void Dynamixel_EnterWheelMode | ( | Dynamixel_HandleTypeDef * | hdynamixel, |
| float | goalVelocity | ||
| ) |
Sets the control registers such that the rotational angle of the motor is not bounded.
When the angle limits are both set to 0, then motor will attempt to rotate with maximum velocity. To prevent undesired behaviour, the goal velocity should be set right after calling this function
- Parameters
-
hdynamixel pointer to a Dynamixel_HandleTypeDef structure that contains the configuration information for the motor goalVelocity the desired velocity in RPM to use when entering wheel mode
- Returns
- None
Definition at line 1023 of file DynamixelProtocolV1.c.